Most people agree that education is one of the most important factors that have transformed human civilisation. It shapes people, societies, and countries by giving them the tools they need to learn, flourish socially, and make money. This article looks at the many different aspects of education, how it has changed throughout time, the problems it faces now, and how important it is for influencing the future. Readers will learn a lot about why education is still important for personal growth and world progress by looking closely at its parts and effects. Importance of education
The Essence of Education
At its core, education is the process by which knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes are passed from one generation to another. It encompasses formal schooling systems, from primary to tertiary levels, as well as informal learning acquired through experience, observation, and self-study. Education is not just about rote memorisation or standardised testing; it involves cultivating critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving abilities, and social awareness.
Philosophers like John Dewey championed education as an active process where learners engage with their environment, fostering experiential and inquiry-based learning. Paulo Freire, a prominent educator and thinker, emphasised education’s role as a liberatory tool that empowers marginalised communities to challenge oppression. These perspectives underline the transformative potential of education far beyond basic literacy and numeracy.
Historical Roots and Evolution of Educational Systems
The concept of formal education dates back thousands of years, traits origins to early civilisationstions such as Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, and Greece. Early societies established schools where elites learnt writing, mathematics, philosophy, and governance. The Classical Greek institutions, like Plato’s Academy and Aristotle’s Lyceum, laid intellectual foundations for Western education. The mediaeval period saw the rise of universities, such as the University of Bologna and the University of Oxford, which formalised curricula and academic degrees.
The Renaissance and Enlightenment eras expanded access to education and promoted scientific inquiry and humanism. This intellectual flourishing paved the way for modern public schooling systems. In the 20th and 21st centuries, education underwent rapid transformations with technological advances. The introduction of computers, the internet, and online learning platforms has revolutionised accessibility and pedagogy. Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) and digital classrooms now allow millions worldwide to pursue education remotely, breaking down geographical and socioeconomic barriers.
The Social and Economic Significance of Education
Education acts as a powerful engine for economic development by equipping individuals with the skills necessary for employment and entrepreneurship. According to human capital theory, popularised by economist Gary Becker, investing in education increases productivity and fosters innovation. Countries with higher educational attainment levels tend to enjoy stronger economic growth, improved health outcomes, and greater social stability.
Moreover, education promotes social cohesion by nurturing shared values, cultural understanding, and civic responsibility. It reduces inequalities by providing pathways for upward mobility and empowering disadvantaged groups. The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals recognise education as fundamental to ending poverty, achieving gender equality, and fostering sustainable communities.
Contemporary Challenges in Education
Despite its critical importance, education systems globally face significant challenges. Access to quality education remains uneven, especially in developing regions affected by poverty, conflict, and insufficient infrastructure. Gender disparities persist in many parts of the world, limiting opportunities for girls and women. The rapid pace of technological and societal change also pressures education systems to remain relevant. We need curriculum reforms to equip students.
Students need to acquire skills such as digital literacy, critical thinking, and adaptability. Teacher shortages and inadequate training hinder effective instruction in many countries. The digital divide presents another hurdle. While online education promises greater accessibility, lack of reliable internet and devices excludes millions from benefiting fully. Additionally, concerns over student engagement and screen fatigue require innovative approaches to balance technology use.
Innovations and Future Directions in Education
To meet these challenges, educators and policymakers are embracing innovative strategies. Personalised learning, powered by artificial intelligence, adapts content and pace to individual learner needs, enhancing effectiveness. Competency-based education shifts focus from seat time to mastery of skills.
New pedagogical methods such as flipped classrooms and project-based learning foster active participation and real-world problem solving. Social-emotional learning (SEL) initiatives address mental health and interpersonal skills, recognising the holistic nature of education.
Technology continues to expand possibilities through virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and gamification, creating immersive and engaging learning experiences. Lifelong learning is increasingly essential as career paths evolve, requiring continual skill updates beyond formal education.
Shaping Modern Education Globally
Throughout history, visionary educators have shaped modern educational philosophies. Maria Montessori developed a child-centred approach emphasising independence and sensory exploration. John Dewey’s progressive education championed democracy and experience as the basis of learning. Paulo Freire’s critical pedagogy highlighted education’s role in social justice and empowerment.
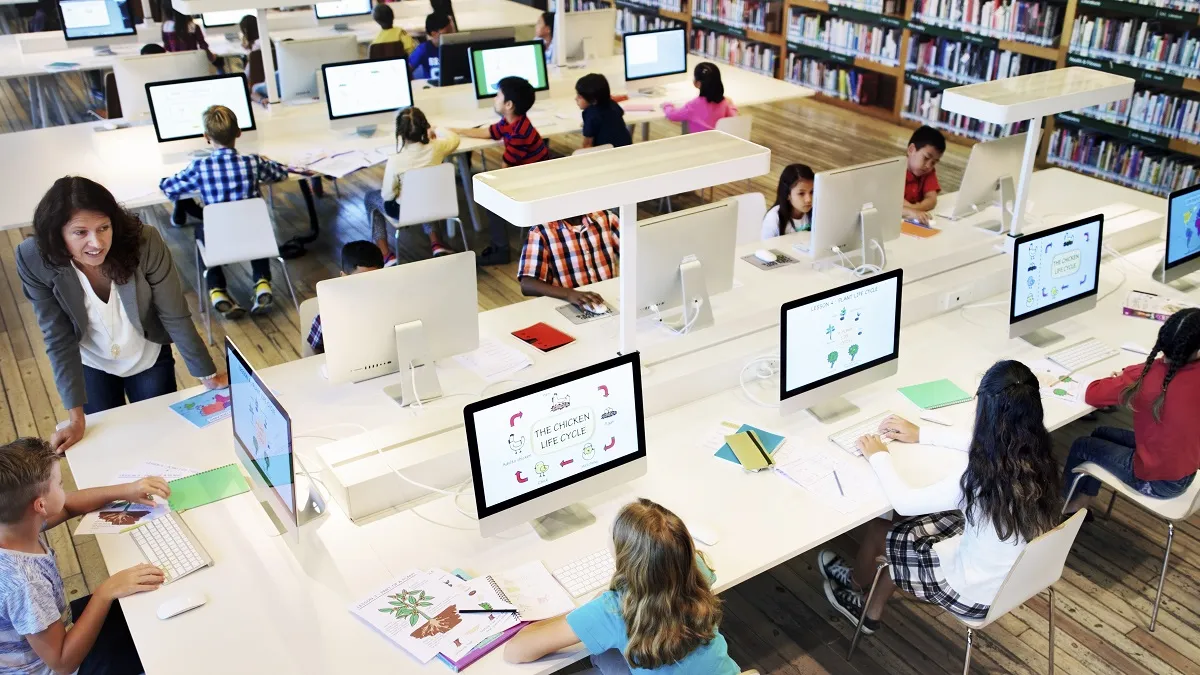

Global organisations, such as UNESCO, play a vital role in promoting education as a universal human right and coordinating international efforts to improve educational quality and access.
Final thoughts
Readers who want to learn more might get useful information by looking into similar subjects, like “The Impact of Digital Technology on Education” and “Lifelong Learning Strategies for Professionals.” Linking to reputable sites like UNESCO’s education portal, the OECD Education Directorate, and World Bank education reports gives you information that is current and reliable.




















