The global supply chain industry faces unprecedented challenges—from counterfeiting and fraud to inefficiencies and lack of transparency. Enter blockchain technology for supply chain management, a revolutionary solution that’s transforming how businesses track, verify, and optimize their logistics operations.
This distributed ledger technology offers unparalleled transparency, security, and efficiency, making it the go-to solution for modern enterprises seeking competitive advantages. With companies losing billions annually to supply chain inefficiencies, blockchain emerges as the transformative technology that addresses these critical pain points while creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
What Is Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management?
Blockchain technology for supply chain management refers to the implementation of distributed ledger systems to record, track, and verify every transaction and movement of goods throughout the entire supply chain network. Unlike traditional databases controlled by single entities, blockchain creates an immutable, transparent record that all authorized participants can access and verify in real-time.
This technology creates a digital chain of custody for products, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. Each transaction or movement gets recorded as a “block” containing detailed information about the product, timestamp, location, and parties involved. Once added to the chain, this information cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring data integrity and accountability.
How Blockchain Works in Supply Chain Operations
The implementation of blockchain in supply chains involves several key components working together seamlessly. Smart contracts automate processes and trigger actions when predetermined conditions are met. For instance, payment can automatically release when goods reach a specific location, verified through IoT sensors connected to the blockchain network.
Distributed nodes across the network validate each transaction, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing processing time. This peer-to-peer verification system ensures that no single party can manipulate data, creating unprecedented trust among supply chain partners who may have never worked together before.
Key Benefits of Using Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
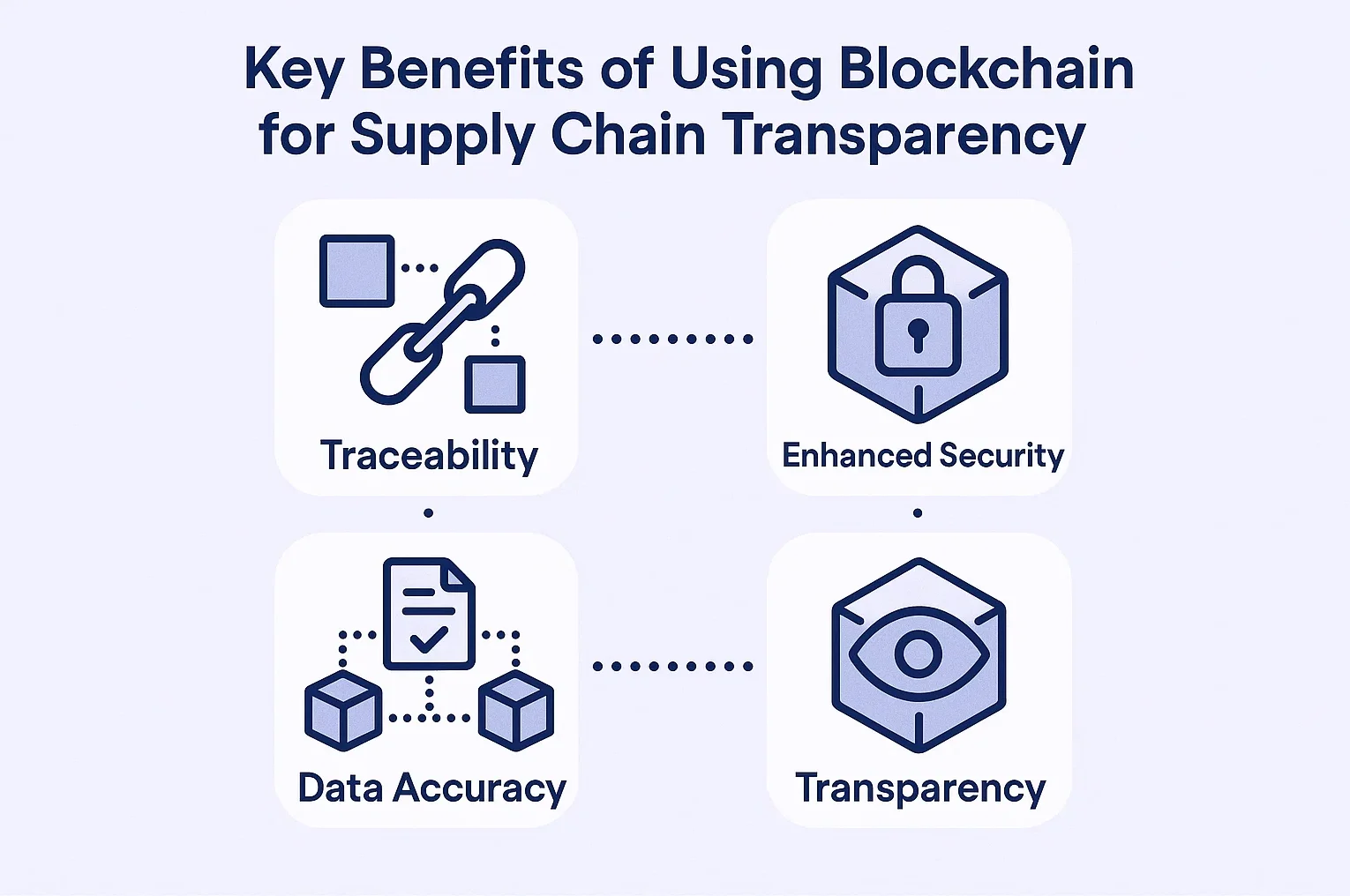
Enhanced transparency stands as perhaps the most compelling advantage of blockchain technology for supply chain management. Every stakeholder—from manufacturers and distributors to retailers and consumers—can trace a product’s journey with complete visibility.
Real-Time Tracking and Visibility
Traditional supply chains operate with information silos, where each participant maintains separate records. Blockchain eliminates these silos by providing a single source of truth accessible to all authorized parties. Companies can monitor shipments in real-time, identify bottlenecks immediately, and make data-driven decisions to optimize operations.
This level of visibility extends beyond location tracking. Organizations can monitor temperature conditions for perishable goods, verify handling procedures, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements throughout the journey. When issues arise, pinpointing the exact location and cause becomes instantaneous rather than taking days or weeks of investigation.
Fraud Prevention and Counterfeit Detection
The pharmaceutical, luxury goods, and electronics industries lose billions annually to counterfeiting. Blockchain creates an unforgeable digital identity for each product, making it virtually impossible for counterfeit items to enter the legitimate supply chain undetected.
Consumers can scan QR codes or use mobile apps to verify product authenticity instantly, checking the complete history from manufacturing to their hands. This capability not only protects brand reputation but also ensures consumer safety, particularly critical for medications and food products.
Implementing Blockchain Solutions in Your Supply Chain
Successfully implementing blockchain technology for supply chain management requires careful planning and strategic execution. Organizations must consider their specific needs, existing infrastructure, and long-term objectives before selecting a blockchain platform.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Platform
Multiple blockchain platforms cater specifically to supply chain applications. Hyperledger Fabric offers enterprise-grade permissioned networks ideal for businesses requiring privacy and control. Ethereum provides smart contract functionality suitable for complex supply chain scenarios requiring automation and programmability.
VeChain specializes in supply chain and business processes, offering ready-to-deploy solutions that integrate with existing systems. IBM Food Trust, built on Hyperledger Fabric, focuses specifically on food supply chain traceability. The choice depends on factors including transaction volume, privacy requirements, scalability needs, and integration complexity.
Steps to Deploy Blockchain in Supply Chain Operations
The deployment process begins with identifying specific pain points and use cases where blockchain delivers maximum value. Rather than attempting to blockchain-ize the entire supply chain immediately, successful implementations typically start with pilot projects targeting high-impact areas.
Next, organizations must establish governance frameworks defining who can access the network, what information gets shared, and how decisions get made. This step proves crucial because blockchain’s value increases with network participation—getting competitors or partners to join requires clear benefits and trust mechanisms.
Technical integration follows, connecting blockchain networks with existing ERP systems, IoT devices, and databases. This integration ensures seamless data flow without disrupting ongoing operations. Organizations should also invest in training staff across all levels, from warehouse workers scanning QR codes to executives interpreting blockchain analytics.
Blockchain Use Cases Transforming Supply Chain Industries
Real-world applications of blockchain technology for supply chain management demonstrate tangible benefits across diverse industries. These success stories provide valuable insights for organizations considering blockchain adoption.
Food Industry Traceability Solutions
Walmart pioneered blockchain adoption in food supply chains, reducing the time needed to trace mangoes from farm to store from seven days to just 2.2 seconds. This capability proves invaluable during food safety incidents, enabling rapid identification of contaminated batches and minimizing health risks.
The system tracks every touchpoint—harvesting, processing, packaging, distribution, and retail—creating an immutable record. When contamination occurs, affected products can be removed from shelves within minutes rather than days, potentially saving lives and reducing financial losses from widespread recalls.
Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Security
Counterfeit medications kill hundreds of thousands annually and cost the industry over $200 billion yearly. Blockchain provides pharmaceutical companies with tools to create tamper-proof digital passports for each medication package.
MediLedger Network brings together major pharmaceutical manufacturers, wholesalers, and pharmacies on a shared blockchain platform. The system verifies product authenticity at each transaction point, ensures compliance with track-and-trace regulations, and prevents illegitimate products from entering the supply chain. Patients can verify their medication’s authenticity using smartphone apps, building trust and ensuring safety.
Automotive Parts Authentication
The automotive industry faces significant challenges with counterfeit parts compromising vehicle safety and performance. BMW and other manufacturers implement blockchain solutions to track parts from suppliers through assembly and eventual vehicle lifetime maintenance records.
This approach ensures only authentic, quality-tested components enter vehicles while creating comprehensive maintenance histories that increase resale value. Service centers can verify parts authenticity before installation, protecting consumers and maintaining brand integrity.
Overcoming Challenges in Blockchain Supply Chain Adoption
Despite its transformative potential, blockchain technology for supply chain management faces several implementation challenges that organizations must address proactively.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Most companies operate with established ERP, WMS, and TMS systems that weren’t designed for blockchain connectivity. Creating middleware solutions that bridge legacy systems with blockchain networks requires significant technical expertise and investment.
The solution involves developing APIs and integration layers that translate data between systems without requiring complete infrastructure overhauls. Organizations should seek blockchain platforms offering pre-built connectors for popular enterprise systems, reducing development time and complexity.
Achieving Network Effect and Collaboration
Blockchain’s value multiplies with network participation, but convincing competitors and partners to join shared networks presents challenges. Companies fear losing competitive advantages by sharing data or worry about governance and control issues.
Successful networks establish clear value propositions for all participants, implement robust privacy controls that protect sensitive information, and create neutral governance structures preventing any single organization from dominating. Consortium blockchains, where multiple organizations jointly govern the network, often prove more acceptable than single-company initiatives.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Public blockchains like Bitcoin process limited transactions per second, unsuitable for high-volume supply chains. However, permissioned enterprise blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric handle thousands of transactions per second, meeting most supply chain requirements.
Organizations must evaluate throughput needs carefully, considering peak transaction volumes and future growth. Hybrid approaches combining public blockchains for verification with private channels for high-volume transactions offer balanced solutions.
Cost Analysis: ROI of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Understanding the financial implications of implementing blockchain technology for supply chain management helps organizations make informed investment decisions and set realistic expectations.
Initial Investment and Implementation Costs
Blockchain implementation costs vary significantly based on scope and complexity. Small pilot projects might cost $50,000 to $200,000, while enterprise-wide deployments can exceed several million dollars. Major cost components include platform licensing, system integration, hardware infrastructure, consulting fees, and training programs.
Organizations should budget for ongoing costs including network maintenance, security updates, transaction fees (for some blockchain platforms), and dedicated personnel to manage blockchain operations. Cloud-based blockchain-as-a-service offerings from providers like IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon reduce upfront infrastructure costs while providing scalability.
Measurable Returns and Cost Savings
Despite significant initial investments, blockchain delivers substantial returns through multiple channels. Reduced fraud and counterfeiting save companies millions annually. Walmart reported 40% reduction in food waste through improved traceability, translating to millions in savings.
Administrative cost reductions occur through automated reconciliation and smart contracts eliminating manual verification processes. Companies report 30-50% reductions in documentation and verification costs. Faster dispute resolution and reduced paperwork free up personnel for value-adding activities.
Improved inventory management through real-time visibility reduces carrying costs and stockouts. Organizations report 10-20% inventory cost reductions after blockchain implementation. Enhanced consumer trust and brand reputation, while harder to quantify, contribute significantly to long-term competitive advantage and market share growth.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Blockchain Supply Chains
The future of blockchain technology for supply chain management promises even greater capabilities as the technology matures and adoption accelerates.
Integration with IoT and AI Technologies
The convergence of blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors creates autonomous supply chains where devices automatically record data directly to blockchain networks. Temperature sensors in refrigerated trucks, GPS trackers on shipping containers, and RFID tags on products feed real-time data into immutable records without human intervention.
Artificial Intelligence analyzes blockchain data to predict demand patterns, optimize routing, identify potential disruptions before they occur, and recommend proactive measures. This combination creates intelligent, self-optimizing supply chains that adapt dynamically to changing conditions.
Sustainability and ESG Compliance
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting requirements intensify globally, pressuring companies to demonstrate sustainable practices throughout supply chains. Blockchain provides verifiable proof of ethical sourcing, carbon footprint tracking, and fair labor practices.
Consumers increasingly demand transparency about product origins and environmental impact. Blockchain enables brands to share verified sustainability credentials, differentiating themselves in competitive markets. Carbon credit trading on blockchain networks creates new mechanisms for companies to achieve net-zero commitments.
Tokenization and Financial Innovation
Tokenization of physical assets on blockchain enables new financing models for supply chains. Small suppliers can tokenize invoices or inventory, accessing working capital faster through decentralized finance platforms. This democratization of supply chain finance reduces dependency on traditional banks and lowers financing costs.
Smart contracts automate payment terms based on verified delivery milestones, improving cash flow for all participants. Cryptocurrency settlements enable instant cross-border payments, eliminating currency conversion fees and reducing transaction times from days to minutes.
Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management: Best Practices
Organizations achieving success with blockchain implementations follow proven best practices that maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Start with Clear Business Objectives
Avoid implementing blockchain simply because competitors are doing so. Identify specific business problems where blockchain’s unique characteristics—immutability, transparency, decentralization—provide superior solutions compared to traditional databases or systems.
Define measurable success metrics before deployment, such as reduced processing time, decreased fraud incidents, improved customer satisfaction scores, or inventory cost reductions. These metrics guide implementation decisions and demonstrate ROI to stakeholders.
Build Collaborative Networks
Blockchain’s value depends on network participation. Invest time in building consortiums with suppliers, distributors, and even competitors who recognize mutual benefits. Establish governance frameworks that ensure fair participation and decision-making.
Provide incentives for network participants, whether through cost-sharing of implementation expenses, improved payment terms, or access to better market intelligence. Networks where all participants gain value grow faster and deliver greater benefits.
Prioritize Interoperability and Standards
The supply chain ecosystem includes numerous blockchain platforms and legacy systems that must communicate effectively. Adopt industry standards for data formats, transaction protocols, and identity management from the beginning.
Participate in industry consortiums and standards organizations shaping blockchain supply chain protocols. This involvement ensures your implementation remains compatible with evolving standards and facilitates future expansion.
Security Considerations for Blockchain Supply Chain Networks
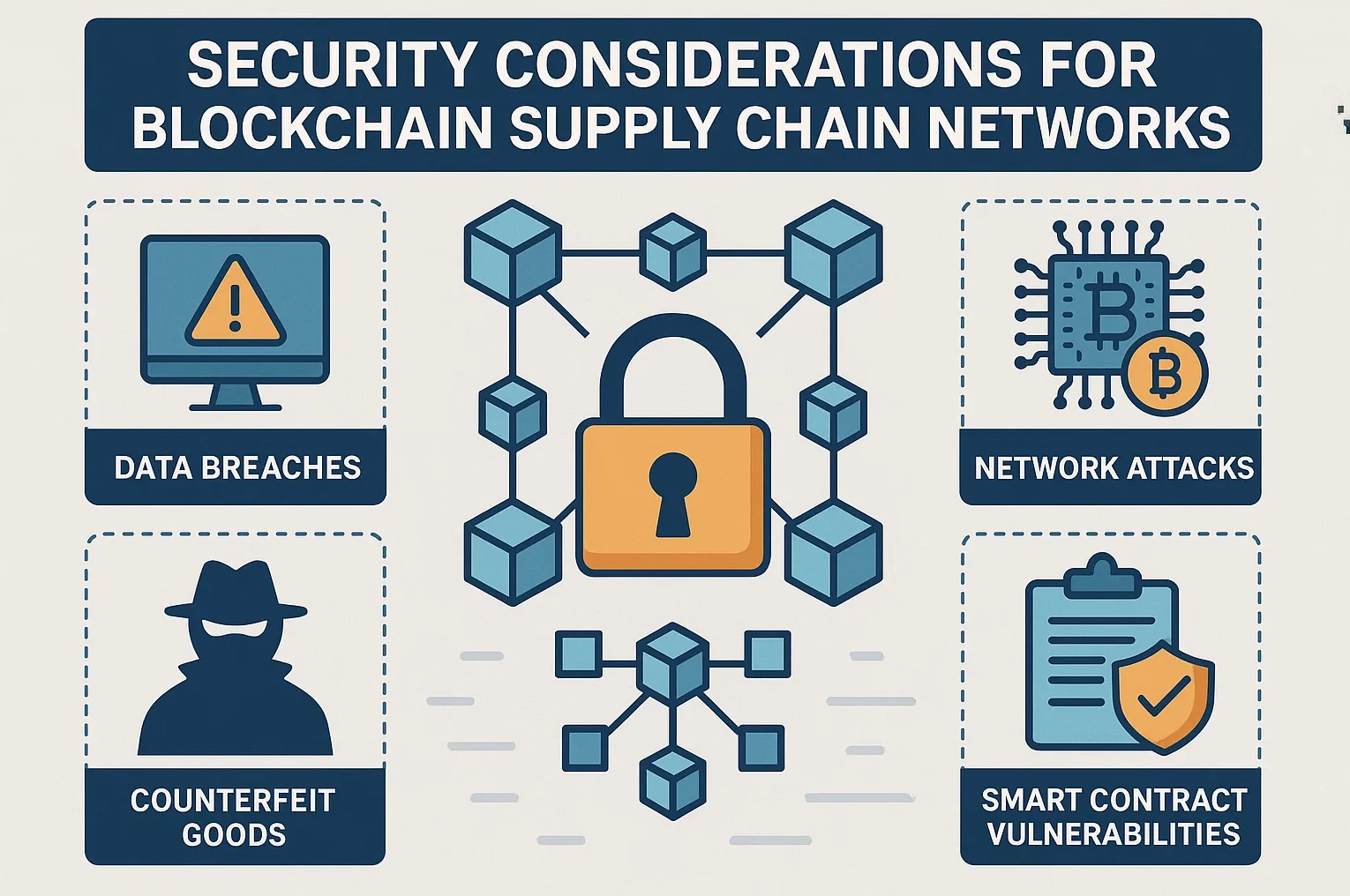
While blockchain offers enhanced security compared to traditional systems, organizations must still address specific security challenges to protect their supply chain networks.
Access Control and Permission Management
Implement robust identity and access management systems determining who can view, add, or validate information on the blockchain. Role-based access ensures suppliers see only relevant portions of the supply chain while preventing unauthorized access to sensitive business data.
Multi-factor authentication, digital certificates, and biometric verification add security layers protecting against unauthorized network access. Regular access audits identify and remove obsolete permissions, maintaining tight security controls.
Smart Contract Security and Auditing
Smart contracts automate supply chain processes but can contain vulnerabilities exploitable by malicious actors. All smart contracts should undergo rigorous security audits by specialized blockchain security firms before deployment.
Implement testing protocols including formal verification methods that mathematically prove smart contract behavior matches specifications. Use established smart contract libraries and frameworks rather than building from scratch, reducing vulnerability risks.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Frameworks
Blockchain technology for supply chain management operates within evolving regulatory environments that organizations must navigate carefully.
Data Privacy and GDPR Considerations
Blockchain’s immutability conflicts with GDPR’s “right to be forgotten” requirement. Organizations must implement solutions like off-chain data storage where blockchain contains only encrypted pointers to personal information that can be deleted when required.
Choose blockchain architectures supporting selective disclosure, where participants control what information they share with whom. Zero-knowledge proofs enable verification without revealing underlying data, balancing transparency with privacy.
Cross-Border Trade Regulations
International supply chains must comply with varying regulations across jurisdictions. Blockchain systems should incorporate regulatory requirements directly into smart contracts, automatically ensuring compliance with import/export restrictions, customs requirements, and trade sanctions.
Work with legal experts specializing in blockchain and international trade to structure implementations that meet regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency. Stay informed about evolving regulations as governments worldwide develop blockchain-specific legal frameworks
Conclusion
The transformation potential of blockchain technology for supply chain management extends far beyond simple tracking improvements. This revolutionary technology creates transparent, efficient, and secure supply chain ecosystems that benefit all participants—from manufacturers and logistics providers to retailers and end consumers.
Organizations implementing blockchain solutions gain competitive advantages through reduced costs, enhanced customer trust, improved sustainability compliance, and operational excellence. As regulatory requirements intensify and consumer expectations rise, blockchain transitions from optional innovation to competitive necessity.
SEE MORE:How Blockchain Technology Transforms Supply Chain Management