Analysis is a powerful intellectual tool that plays a pivotal role across numerous fields, from science and technology to literature and business. The process of analysis involves breaking down complex information into understandable components, enabling deeper insight and informed decision-making. This article gives an in-depth primer on analysis, highlighting its varied methods, applications, and significance in today’s data-driven world. By exploring semantic SEO principles such as keyword clustering and topical relevance, this content also aims to serve as an authoritative resource for users with diverse intents. analysis methods and applications
Defining Analysis and Its Fundamental Role
In its simplest form, analysis is the process of looking closely at something to figure out how it works, what its parts are, and what its basic ideas are. The word comes from the Greek word “analusis”, which means “to loosen”, “to come apart”, or “to separate”. Analysis helps turn raw data into useful knowledge, whether you’re looking at financial accounts, figuring out the themes in a book, or making sense of scientific facts. analysis methods and applications
To understand the subtleties of analysis, you first need to know what it is for: to make things clearer, find patterns, and back up conclusions. In finance, for instance, looking at stock market trends helps investors like Warren Buffett make smart choices. Literary analysis also finds symbols and cultural settings in classic works like Shakespeare’s plays that make them more captivating to read.
Varieties of Analysis Across Disciplines
The forms of analysis are diverse, each tailored to specific types of data and objectives. Data analysis is among the most prevalent forms, especially in an era dominated by big data and artificial intelligence. This process involves collecting, cleaning, and modelling data to uncover trends and insights. Popular tools such as Python’s Pandas and R, and software like Tableau, enable data professionals to visualise complex datasets and perform predictive analytics.
Qualitative analysis differs from its quantitative counterpart by focusing on non-numerical data such as interviews, open-ended survey responses, and textual information. Techniques like thematic and discourse analyses help researchers understand social phenomena, behaviours, and opinions. For instance, in marketing research, qualitative analysis can reveal customer sentiment, guiding brand strategies for companies like Nike or Coca-Cola. analysis methods and applications
In scientific fields, analysis often takes the form of experimental and statistical examination. Researchers like Marie Curie and Isaac Newton relied on meticulous analytical methods to formulate groundbreaking theories. The scientific method, which underpins empirical inquiry, is essentially an iterative process of hypothesising, experimenting, observing, and analysing results.
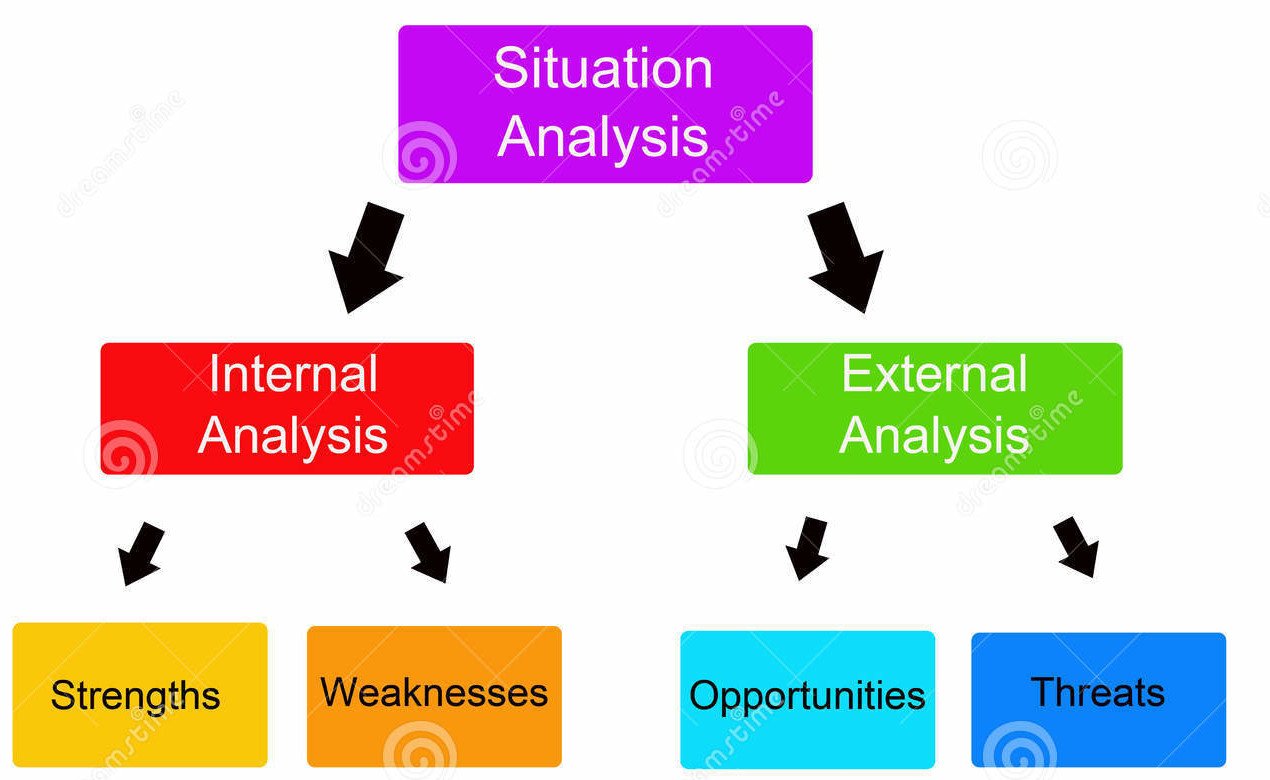
Business analysis, a key function within corporate strategy, involves evaluating internal and external factors to optimise performance. Tools such as SWOT analysis help organisations like Amazon assess strengths and weaknesses alongside market opportunities and threats, informing strategic planning.
The Impact of Technology on Analytical Processes
Modern technology has revolutionised analysis by enhancing both speed and accuracy. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are now integral to processing vast quantities of data. Cloud platforms like Google Cloud AI and Microsoft Azure provide scalable environments for complex analyses, enabling real-time insights that were previously unattainable.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has also expanded the scope of analysis, allowing computers to interpret and categorise human language. This technology powers sentiment analysis used in social media monitoring and customer service, helping brands respond swiftly to public opinion. Furthermore, data visualisation tools such as Power BI and D3.js transform raw data into interactive graphics, making complex results accessible to a broader audience.
Emerging technologies like blockchain analytics are increasingly used to trace cryptocurrency transactions and enhance transparency in financial systems. The fusion of analytical methods with these technologies is driving innovation across sectors from healthcare to manufacturing.
Semantic SEO and the Role of Analysis in Digital Content
In the digital realm, analysis extends beyond traditional disciplines to optimise content for search engines. Semantic SEO focuses on clustering related keywords and using Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) terms to deepen topical relevance. For instance, an article about analysis might naturally incorporate keywords such as “data interpretation”, “critical thinking”, “analytical methods”, and “pattern recognition”.
Employing a clear heading hierarchy with H1, H2, and H3 tags enhances both readability and search engine comprehension. Rich entities—such as references to notable figures like Alan Turing, technological tools like Tableau, and relevant concepts like big data—enrich the semantic value of content, making it more authoritative and user-friendly. Content creators can improve internal linking by connecting related articles, for example, “Introduction to Data Science”, “The Importance of Critical Thinking”, and “Emerging Technologies in Analytics”. External references to reputable sites like Harvard Business Review or the Journal of Data Science add credibility and provide readers with pathways for further exploration.
Addressing Multiple User Intents in Analysis
When users search for “analysis,”, their intentions may vary widely. Some seek foundational knowledge about what analysis entails, while others look for practical applications or software recommendations. Some may desire historical perspectives on analytical methods, whereas others want to understand emerging trends.  By covering these aspects comprehensively, this article meets diverse needs. It provides conceptual clarity for students and researchers, practical insights for professionals, and contextual background for enthusiasts. Such an approach increases engagement and ensures the content ranks well across a broad range of relevant search queries.
By covering these aspects comprehensively, this article meets diverse needs. It provides conceptual clarity for students and researchers, practical insights for professionals, and contextual background for enthusiasts. Such an approach increases engagement and ensures the content ranks well across a broad range of relevant search queries.
Final thoughts
Technological progress has a big impact on the future of analysis. XAI, or Explainable AI, wants to make automated decision-making more clear and reliable. Real-time analytics and edge computing make it possible to process data right at the source, which is beneficial for industries like healthcare and smart manufacturing.
As technology gets better, moral problems become more important. Organisations need to follow tight rules because they are concerned about data protection, algorithmic biases, and the ethical use of AI. As analysis becomes more complicated and a part of everyday life, it becomes vitally important to find a balance between new ideas and moral responsibility.




















