The global supply chain industry is experiencing a revolutionary transformation, and blockchain technology for supply chain management stands at the forefront of this evolution. As businesses struggle with transparency issues, counterfeit products, and complex logistics networks, blockchain emerges as the ultimate solution to address these persistent challenges. This distributed ledger technology promises unprecedented visibility, enhanced security, and streamlined operations across entire supply chains.
Modern supply chains involve countless stakeholders, from manufacturers and suppliers to distributors and retailers. Traditional methods of tracking goods and verifying authenticity often fall short, leaving gaps that criminals exploit and consumers suffer. However, blockchain technology for supply chain management offers an immutable, transparent ledger that records every transaction and movement, creating an unbreakable chain of custody that benefits everyone involved.
What is Blockchain Technology for Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology for supply chain management represents a paradigm shift in how businesses track, verify, and manage their products throughout the entire journey from raw materials to end consumers. This revolutionary approach utilizes distributed ledger technology to create an immutable record of every transaction, movement, and transformation that occurs within the supply chain network.
Unlike traditional centralized databases that can be manipulated or corrupted, blockchain creates a decentralized system where every participant maintains a copy of the complete transaction history. Each block in the chain contains cryptographically secured information about products, including their origin, manufacturing details, quality certifications, and ownership transfers.
The technology operates on consensus mechanisms, ensuring that all network participants agree on the validity of transactions before they’re permanently recorded. This eliminates the possibility of fraudulent entries and creates an unprecedented level of trust among supply chain partners.
Key Components of Blockchain Supply Chain Systems
Blockchain supply chain solutions consist of several interconnected components that work together to ensure seamless operations:
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automatically trigger actions when predetermined conditions are met. For example, payment can be released automatically when goods reach their destination and pass quality checks.
IoT Integration: Internet of Things devices capture real-time data about product conditions, location, and environmental factors, feeding this information directly into the blockchain.
Digital Identity Management: Each product receives a unique digital identity that follows it throughout its journey, making counterfeiting virtually impossible.
Consensus Mechanisms: These protocols ensure all network participants agree on transaction validity before recording them permanently.
How Blockchain Transforms Supply Chain Transparency
Traditional supply chains operate like black boxes, where information flow is fragmented and often incomplete. Blockchain technology for supply chain management illuminates these dark corners by providing complete visibility into every aspect of the product journey.
When a manufacturer creates a product, they register it on the blockchain with detailed specifications, quality certifications, and manufacturing data. As the product moves through different stages—transportation, warehousing, distribution—each stakeholder updates the blockchain with relevant information. This creates an comprehensive audit trail that anyone with appropriate permissions can access instantly.
The transparency extends beyond simple tracking. Consumers can scan QR codes or use mobile apps to access the complete history of their purchased products, including ethical sourcing information, environmental impact data, and quality certifications. This level of transparency builds consumer trust and enables informed purchasing decisions.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Blockchain supply chain solutions incorporate real-time monitoring capabilities that provide instant alerts when issues arise. If a temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical shipment experiences temperature fluctuations beyond acceptable ranges, the system immediately notifies all relevant parties and triggers appropriate responses.
This proactive approach prevents quality issues from escalating and enables swift corrective actions. Supply chain managers can identify bottlenecks, delays, or quality issues before they impact customer satisfaction or regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
The implementation of blockchain technology for supply chain management delivers transformative benefits that address longstanding industry challenges while opening new opportunities for optimization and growth.
Enhanced Traceability and Product Authentication
Blockchain creates an unbreakable chain of custody that makes counterfeiting extremely difficult. Each product receives a unique digital fingerprint that cannot be replicated or altered. When consumers purchase products, they can verify authenticity by checking the blockchain record, ensuring they receive genuine items.
This level of traceability proves invaluable during product recalls. Instead of broad, expensive recalls that affect entire product lines, companies can precisely identify affected batches and trace them to specific locations, minimizing costs and consumer impact.
Improved Supplier Verification and Compliance
Traditional supplier verification processes are time-consuming and often incomplete. Blockchain enables automated compliance checking by maintaining permanent records of supplier certifications, audit results, and performance metrics. New suppliers can demonstrate their credentials through blockchain-verified documentation, streamlining the onboarding process.
Regulatory compliance becomes more manageable when all relevant documentation exists on an immutable ledger. Auditors can access complete compliance histories instantly, reducing audit time and costs while improving accuracy.
Reduced Counterfeiting and Fraud
Counterfeit products cost the global economy hundreds of billions of dollars annually while endangering consumer safety. Blockchain technology for supply chain management creates insurmountable barriers for counterfeiters by establishing authentic product identities that cannot be duplicated.
Each genuine product carries blockchain-verified credentials that prove its authenticity. Retailers and consumers can instantly verify product legitimacy, effectively eliminating the market for counterfeit goods in blockchain-enabled supply chains.
Streamlined Payment and Settlement Processes
Smart contracts automate payment processes based on predetermined conditions, reducing administrative overhead and improving cash flow. When shipments arrive and pass quality inspections, payments are released automatically, eliminating delays associated with manual processing. This automation extends to complex multi-party transactions where payments depend on multiple conditions being met. The blockchain orchestrates these interactions seamlessly, ensuring all parties fulfill their obligations before payments are processed.
Key Use Cases and Industry Applications
Food and Agriculture Supply Chains
The food industry faces unique challenges related to safety, freshness, and organic certification verification. Blockchain technology for supply chain management addresses these issues by creating farm-to-fork traceability that captures every step of the food production and distribution process.
Organic food producers can prove their certification authenticity through blockchain records, while consumers gain confidence in their purchasing decisions. During foodborne illness outbreaks, health authorities can quickly trace contamination sources and implement targeted responses instead of broad industry shutdowns.
Major food retailers are already implementing blockchain solutions to enhance food safety and consumer trust. These systems track products from farms through processing facilities, distribution centers, and retail locations, creating comprehensive visibility into food supply chains.
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Products
Pharmaceutical supply chains require stringent controls to prevent counterfeit drugs from entering the market. Blockchain creates secure, tamper-proof records that verify drug authenticity and ensure proper storage conditions throughout transportation. Temperature-sensitive medications benefit from blockchain integration with IoT sensors that monitor storage conditions continuously.
If temperature deviations occur, the blockchain records these events permanently, enabling quality assessments and preventing compromised medications from reaching patients. Clinical trial supply chains also benefit from blockchain transparency, ensuring research integrity and regulatory compliance while protecting patient safety through verified product authenticity.
Luxury Goods and Fashion Industry
High-end fashion brands lose billions annually to counterfeiting, while consumers struggle to verify authentic luxury items. Blockchain technology for supply chain management provides definitive proof of authenticity through unalterable digital certificates. Each luxury item receives a blockchain-based digital passport that documents its creation, materials, craftsmanship, and ownership history.
This creates significant value for authentic products while making counterfeiting economically unfeasible. Sustainable fashion brands use blockchain to verify their environmental and ethical claims, providing transparent documentation of sustainable sourcing practices and fair labor conditions.
Automotive Industry Supply Chains
Modern vehicles contain thousands of components from hundreds of suppliers, making traditional quality control and recall management extremely complex. Blockchain creates comprehensive component traceability that improves quality control and enables precise recall management.
When safety issues arise, manufacturers can identify affected vehicles precisely and implement targeted fixes instead of costly blanket recalls. This precision reduces costs while improving consumer safety and satisfaction. Electric vehicle battery supply chains benefit particularly from blockchain transparency, ensuring ethical sourcing of rare earth materials and providing complete lifecycle tracking for battery recycling and disposal.
Implementation Strategies for Blockchain Supply Chain Solutions
Successfully implementing blockchain technology for supply chain management requires careful planning, stakeholder alignment, and phased rollout strategies that minimize disruption while maximizing benefits.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Begin implementation by conducting thorough assessments of existing supply chain processes, identifying pain points that blockchain can address effectively. Evaluate current technology infrastructure and determine integration requirements for seamless blockchain adoption. Stakeholder mapping identifies all supply chain participants and their specific needs, ensuring the blockchain solution addresses everyone’s requirements. This collaborative approach increases adoption rates and maximizes network effects.
Technology Selection and Integration
Choose blockchain platforms that align with your supply chain’s specific requirements. Public blockchains offer maximum transparency but may raise privacy concerns, while private or consortium blockchains provide controlled access suitable for sensitive business operations. Integration with existing enterprise systems requires careful planning to ensure data consistency and workflow continuity. APIs and middleware solutions facilitate smooth connections between blockchain networks and traditional business systems.
Pilot Program Development
Start with limited-scope pilot programs that demonstrate blockchain value without overwhelming existing operations. Select high-impact use cases that deliver measurable benefits quickly, building momentum for broader implementation. Pilot programs should include representative stakeholders from across the supply chain, ensuring the solution works effectively in real-world conditions. Gather feedback continuously and refine the system based on user experiences.
Scaling and Network Expansion
After successful pilot validation, gradually expand blockchain implementation across broader supply chain networks. Prioritize critical suppliers and high-value product lines that benefit most from enhanced transparency and security. Network effects increase blockchain value as more participants join, creating positive feedback loops that encourage additional adoption. Incentive programs can accelerate network growth by highlighting tangible benefits for early adopters.
Challenges and Solutions in Blockchain Supply Chain Implementation
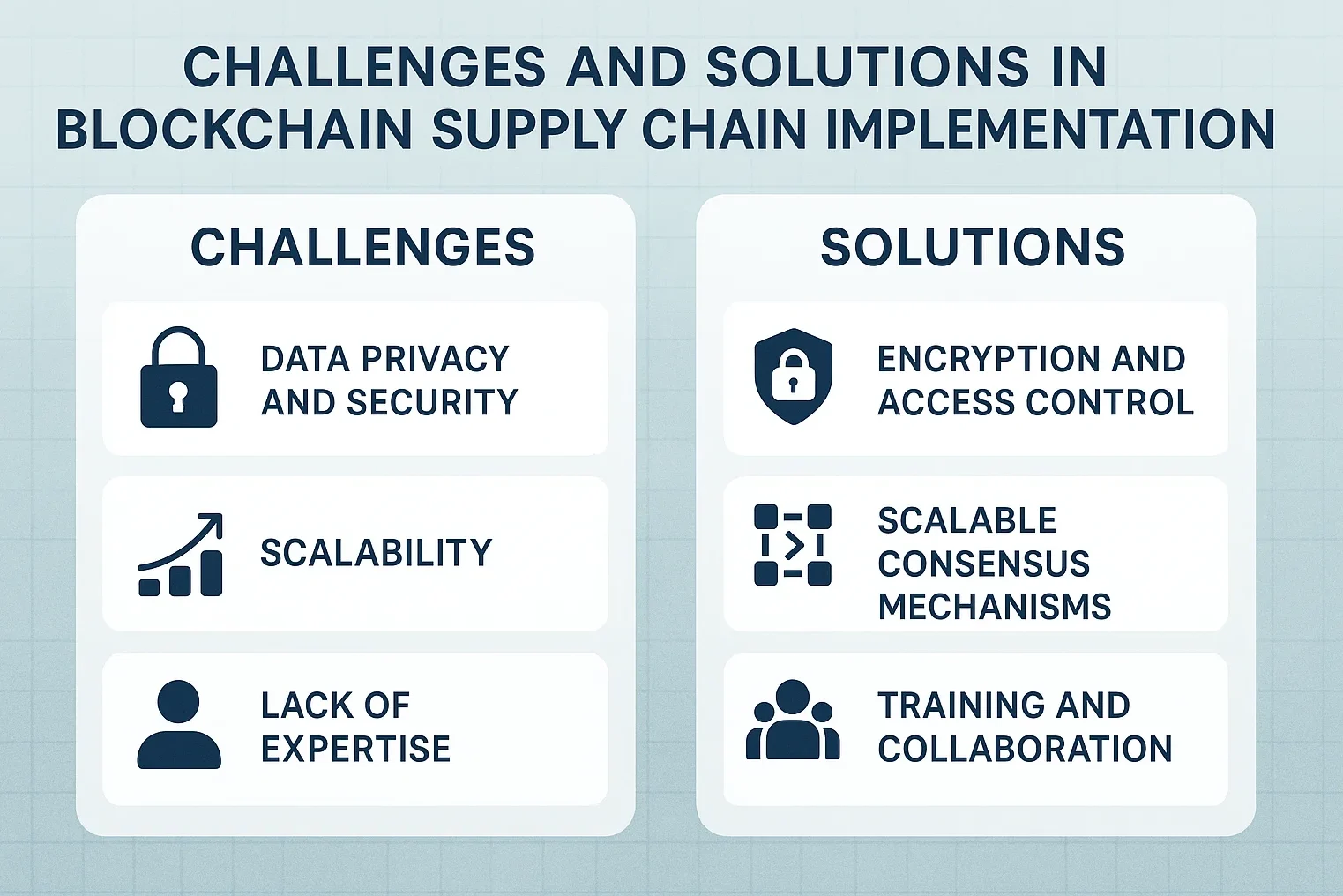
Technical Integration Complexities
Legacy systems integration presents significant challenges when implementing blockchain technology for supply chain management. Many organizations operate on decades-old systems that weren’t designed for blockchain connectivity.
Solution: Implement middleware solutions and APIs that bridge legacy systems with blockchain networks. Gradual migration strategies allow organizations to maintain operations while modernizing incrementally.
Scalability and Performance Concerns
Traditional blockchain networks may struggle with the high transaction volumes typical in global supply chains. Processing thousands of transactions per second while maintaining security and decentralization requires careful architecture design.
Solution: Hybrid blockchain architectures combine public and private networks to optimize performance while maintaining necessary transparency. Layer-2 solutions and sidechains can handle high-volume transactions efficiently.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Different jurisdictions have varying regulations regarding data storage, privacy, and blockchain usage. International supply chains must navigate complex regulatory landscapes while maintaining compliance across multiple territories.
Solution: Work with legal experts to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Design flexible systems that can adapt to changing regulatory requirements while maintaining core functionality.
Cost and ROI Considerations
Initial blockchain implementation requires significant investment in technology, training, and process modification. Organizations need clear ROI projections to justify these investments to stakeholders.
Solution: Focus on high-impact use cases that deliver measurable benefits quickly. Quantify savings from reduced fraud, improved efficiency, and enhanced customer trust to demonstrate clear ROI.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of blockchain technology for supply chain management promises exciting developments that will further enhance capabilities and expand adoption across industries.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence algorithms will analyze blockchain supply chain data to identify patterns, predict disruptions, and optimize routing decisions. Machine learning models will continuously improve supply chain efficiency based on historical blockchain data. Predictive analytics will enable proactive supply chain management, identifying potential issues before they occur and recommending optimal solutions. This combination of blockchain transparency and AI insights creates unprecedented supply chain intelligence.
Enhanced IoT Integration
Internet of Things devices will become more sophisticated and affordable, enabling comprehensive real-time monitoring of products throughout their journey. Smart sensors will capture environmental data, location information, and condition metrics continuously. Edge computing will process IoT data locally before recording summaries on the blockchain, reducing network congestion while maintaining comprehensive monitoring capabilities.
Sustainability and Carbon Tracking
Environmental consciousness drives demand for transparent carbon footprint tracking throughout supply chains. Blockchain technology for supply chain management will evolve to capture and verify environmental impact data comprehensively. Carbon credit systems will integrate with supply chain blockchains, enabling automated carbon offset transactions based on verified environmental impact data. This creates market incentives for sustainable supply chain practices.
Interoperability Standards
Industry standards will emerge to ensure blockchain supply chain systems can communicate effectively across different platforms and organizations. These standards will facilitate broader adoption and network effects. Cross-chain protocols will enable seamless data sharing between different blockchain networks, creating comprehensive supply chain visibility even when participants use different blockchain platforms.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology for supply chain management represents a transformative solution that addresses longstanding industry challenges while creating new opportunities for efficiency, transparency, and consumer trust. As businesses face increasing pressure to demonstrate sustainability, authenticity, and ethical practices, blockchain provides the transparent infrastructure necessary to meet these demands effectively.
The technology’s ability to create immutable records, prevent counterfeiting, and enable real-time tracking makes it invaluable across diverse industries. From ensuring food safety to verifying luxury goods authenticity, blockchain supply chain solutions deliver measurable benefits that justify implementation investments
LEARN MORE:How Blockchain Technology Transforms Supply Chain Management